tibial torsion test physiopedia|how to measure tibial torsion : traders Craig's test is a passive test that is used to measure femoral anteversion or forward torsion of the femoral neck. It is also known as 'Trochanteric Prominence . See more Resultado da Cópia do JOGO DA MEMÓRIA - letra cursiva. Compartilhar Compartilhar de U33021109. Mostrar mais. Editar conteúdo. Incorporar. Mais. Ranking. Mostrar mais Mostrar menos . Atualmente, este ranking é particular. Clique em Compartilhar para torná-lo público. Este ranking foi desativado pelo .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Conforme já mencionado, a fusão renal ocorre quando uma parte de um rim está ligado ao outro rim. O rim em ferradura é a anomalia de fusão mais comum que existe, atingindo 1 em cada 500 crianças. No caso do rim em ferradura, além do defeito da migração de ambos os rins, ocorre a fusão de um ao outro. Os rins fundidos ficam ligados por .
Craig's test is a passive test that is used to measure femoral anteversion or forward torsion of the femoral neck. It is also known as 'Trochanteric Prominence . See moreTo measure internal or external tibial torsion, the patient is positioned in prone lying with knees flexed to 90 o. A thigh-foot ankle (TFA) is measured between the line bisecting the posterior thigh and another line bisecting the foot.
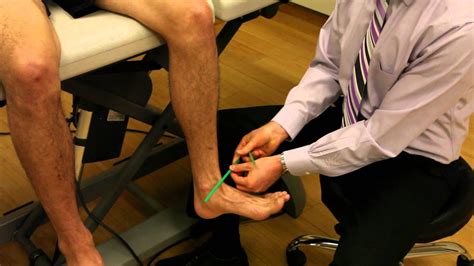
Thigh-foot angle (TFA): a means to measure tibial torsion. To measure internal or external tibial torsion, the patient is positioned in prone lying with their knees flexed to 90° and foot resting in its natural position. The TFA is measured .Tibial torsion is inward twisting of the tibia (shinbone) and is the most common cause of intoeing. It is usually seen at age 2 years. About two thirds of patients are affected bilaterally. .
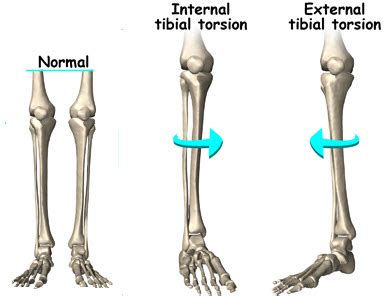
Internal Tibial Torsion is a common condition in children less than age 4 which typically presents with internal rotation of the tibia and an in-toeing gait. Diagnosis is made clinically with a thigh-foot angle > 10 degrees of .Tibial torsion is the twisting of a child’s shinbone, also known as the tibia. In most cases, tibial torsion causes a toddler’s legs and feet to turn inward (internal tibial torsion), giving them a pigeon-toed appearance. Less often, the legs turn .
Dr. Rome explains how to look for tibial torsion, or tibial rotation, with the knee at a 90 degree angle.Persistent, excessive torsion can lead to toeing-in and bowlegs. To evaluate for tibial torsion, the angle between the axis of the foot and the axis of the thigh is measured with the child prone .
9. Images. summary. Femoral Anteversion is a common congenital condition caused by intrauterine positioning which lead to increased anteversion of the femoral neck relative to the femur with compensatory .
Dial Test: 30* knee flexion, Tibial external rotation Dial test video provided by Clinically Relevant Look for posterior sag, and apply anterior force if supine or test prone for neutral tibial positioning.PFPS can also be due to knee hyperextension, lateral tibial torsion, genu valgum or varus, increased Q-angle, tightness in the iliotibial band, hamstrings or gastrocnemius. (see table 1) Sometimes the pain and discomfort is localized in .Clinically Relevant Anatomy [edit | edit source]. The patella is the largest sesamoid bone. It is located within the complex of the quadriceps and patellar tendon. Through its articulation with the femoral trochlea, the patellofemoral .The tibial tubercle (the tuberosity of the tibia) is the protuberance along the anterior aspect of the tibia, just distal to the anterior surfaces of the medial and lateral tibial condyles. The tibial tubercle is entirely cartilaginous. It gives .
Physiopedia articles are best used to find the original sources of information (see the references list at the bottom of the article). . The tibial nerve is the larger terminal branch of the two main muscular branches of the sciatic nerve. It arises from Ventral (anterior) division of L4-5, S1-3. It travels along the distal border of the .
moisture meter pin reading chart
tibial torsion special test
Anatomy of the Meniscus [edit | edit source]. The meniscus is C-shaped cartilage that acts as a cushion between the proximal tibia and the distal femur to make up the knee joint. It has an average width of 10 mm to 12 mm, and the average thickness is 4 mm to 5 mm. The meniscus is made of fibro-elastic cartilage. It is an interlacing network of collagen, proteoglycan, . Dr. Rome explains how to look for tibial torsion, or tibial rotation, with the knee at a 90 degree angle. Special thank you to Dr. Matthew Rome and Equilibri.
Tibial torsion can be assessed by comparing the bimalleolar axis with the position of the tibial tubercle. Note the foot shape: Metatarsus adductus may be the primary cause of in-toeing, particularly in the infant.Tibial torsion occurs if the child's lower leg (tibia) twists inward. This can occur before birth, as the legs rotate to fit in the confined (limited) space of the womb. After birth, an infant's legs should gradually rotate to align properly. If the lower leg remains turned in, the result is tibial torsion.Femoral anteversion or medial torsion of the femur is a condition that changes the alignment of the bones at the knee. This may lead to overuse injuries of the knee due to malalignment of the femur to the patella and tibia. The Q-angle: or quadriceps angle is the geometric relationship between the pelvis, the tibia, the patella and the femur and is defined as the angle between .
A positive test result is when there is greater than 5 mm of anterior motion of the STJ as compared with the non-injured ankle. An audible clunk may also be present during test. Due to increased pain and swelling acutely, the anterior drawer test has been found to have a markedly increased sensitivity when performed 4 to 5 days after injury.
In most cases Physiopedia articles are a secondary source and so should not be used as references. Physiopedia articles are best used to find the original sources of information (see the references list at the bottom of the article). . External tibial torsion; Laterally displaced tibial tubercle; . ↑ Buckup K.Clinical test for .The menisci are fibrocartilaginous structures that function to deepen the tibial plateau, improve articulation of the femur on the tibia, stabilize the knee, and assist with shock absorption. The medial meniscus specifically forms almost a semicircular shape and covers 50-60% of the articular surface between the medial femoral condyle and the .Achilles tendinopathy (common overuse injury) refers to a combination of pathological changes affecting the Achilles tendon usually due to overuse and excessive chronic stress upon the tendon. It can be seen both in athletes and non-athletes. It may or may not be associated with an Achilles tendon tear.A lack of flexibility or a stiff Achilles tendon can increase the risk of these .
trochanteric prominence angle test . . tibial torsion. look at thigh-foot angle in prone position. normal value in infants- mean 5° internal (range, −30° to +20°) normal value at age 8 years- mean 10° external (range, −5° to +30°) metatarsus adductus.Physiopedia articles are best used to find the original sources of information (see the references list at the bottom of the article). . The motor supply to the muscles comes from the tibial, deep peroneal, and superficial peroneal nerves. The .
Single-leg squat (SLS) is a functional test, visually rated by clinicians, for assessing lower limb function as a preventive injury strategy.SLS clinical rating is a qualitative evaluation and it does not count objective outcomes as .
Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome (TTS) is a rare compressive neuropathy of the tibial nerve or one of its branches as they pass under the flexor retinaculum. In the TTS literature, the tibial nerve is also referred to as the posterior tibial nerve and TTS is also known as .Tibial torsion can be external (lateral) or internal (medial). (See also Introduction to Congenital Craniofacial and Musculoskeletal Disorders.) External tibial torsion occurs normally with growth: from 0 ° at birth to 20 ° by adulthood. External torsion is rarely a problem. Internal tibial torsion is common at birth, but it typically .
tibial torsion in adults
Definition / description [edit | edit source]. Patellar malalignment is a translational or rotational deviation of the patella to any axis, associated with several soft-tissue and osteochondral abnormalities and mostly characterised by a tilted and lateral displaced patella. Clinically relevant anatomy [edit | edit source]. The normal translational movement of the patella in the fossa .Valgus knee, or "knock knee", is a deformity of the lower leg where the knee joint angles outward from the body's midline.This condition is defined by a valgus angle of 10° or more.This deformity results from anatomical variations, including bone tissue remodeling and soft tissue contraction or elongation.. Bone tissue remodeling [edit | edit source]Introduction [edit | edit source]. The tibia is a medial and large long bone of the lower extremity, connecting the knee and ankle joints. It is considered to be the second largest bone in the body and it plays an important role in weight bearing. Osteologic features of the tibia include medial and lateral condyles, the tibial plateau, the tibial tuberosity, the soleal line, the medial .
In most cases Physiopedia articles are a secondary source and so should not be used as references. Physiopedia articles are best used to find the original sources of information (see the references list at the bottom of the article). . This is due to the successive use of the three positions of the tibial rotation. The pivot shift test has .The calcaneus, navicular, talus, first three cuneiforms, and the first three metatarsals make up the medial longitudinal arch. This arch is supported by posterior tibial tendon, plantar calcanea navicular ligament, deltoid ligament, plantar aponeurosis, and flexor hallucis longus and brevis muscles. Dysfunction or injury to any of these structures may cause acquired pes planus.Physiopedia articles are best used to find the original sources of information (see the references list at the bottom of the article). If you believe that this Physiopedia article is the primary source for the information you are refering to, you can use the button below to access a related citation statement. Cite articleThe Sacroiliac joint (commonly referred to as SIJ) is the joint connection between the spine and the pelvis. Large diarthrodial joint made up of the sacrum and the two innominates of the pelvis.; Each innominate is formed by the fusion of the three bones of the pelvis: the ilium, ischium, and pubic bone.; The sacroiliac joints are essential for effective load transfer between the spine .
2. A positive drawer test done 5 days after the injury, has been shown to be more sensitive and specific than the test done withing the 24-48 hours. 3. A sensitivity of 52% has been reported in a single study for the inversion talar tilt test. 4. In acute injuries, the eversion stress test may be of limited clinical value.Physiopedia articles are best used to find the original sources of information (see the references list at the bottom of the article). . The reliability of the radiographic talar tilt test was evaluated using MRI in 112 athletes with injuries to the lateral ligaments of the ankle. Twenty-five athletes with a talar tilt of 15" were treated .
moisture meter pins
web25 de out. de 2023 · O caso foi registrado como tentativa de homicídio. O ex-ator mirim Guilhermo Hundadze, de 25 anos, baleado por um policial militar durante briga de .
tibial torsion test physiopedia|how to measure tibial torsion